Home » Janssen Pharmaceutics
Categorie archief: Janssen Pharmaceutics
Cheaper drugs
In the newspaper of the 26 of March, I read that drugs are going to become cheaper. The government is trying to make 2,500 drugs of all kinds cheaper (chronical treatments such as diabetes but also antibiotics and the contraceptive pill), as the minister of Public Health Laurette Onkelinx (PS).says. For some drugs the price reduction can be 50, 60 or even 70%, but she indicates that it is the only way to make drugs available for everybody. Last year, a reduction of the 1.95% was required to fit the budget agreement. Later on an even harder reduction was necessary by the obligated comparison within six European countries. as expected, the pharmaceutical sector was not really pleased with this fact, and the negotiations did not go easily. This is a strong sector, and it provides about 31,000 people with work. For this reason, a consensus had to be found: the prices are going to be reduced and the companies get support in their research. Since the first of April, the new prices are legit, and a saving of ten million Euros should be accomplished.
I think this is a lice initiative, but the problem is only shoved around instead of taken care of. The pharmaceutical sector is trying to innovate and make better drugs, improve existing drugs and invent new ones. As there are still a lot of diseases that cannot be cured, or resistant variants of the disease are developed, the pharmaceutical sector will always need to be able to respond to this. A second remark, is the fact that, once a drug is developed, it is only patented for a certain period. After this period other companies can make the drug as well, and use it as a base for new drug development, or homeopathic variants of the drugs can be made. These all have a great impact on the pharmaceutical sector. As I already said in a previous post, the employees of Janssen are afraid of losing their job, since the division of Springhouse had closed its R&D site. This is another slap in the face for these employees. If they lose their job, the lower prices of drugs will not concern them that much, and an even harder decrease will be necessary as the unemployment will increase.
Innovation
In the R&D, it is not unusual to work with external partners. It is thanks to innovation that it is possible to share ideas, have opinions and be able to change your original vision. This is made possible by the establishment of C.R.E.A.T.e or ‘Community of Research Excellence & Advanced Technology’ that has taken an important step towards the extension of an innovative discovery organization on world scale. In the past, every research team and every pharmaceutical actor, behaved like it was on an island, where the results never left. By the use of an open innovative environment, everything is possible these days.
CREATe plays the role of partner and integrator within Janssen. By working international together with about 350 people, equally divided in Europe and the US, it is possible to share ideas with the world. The assignment of CREATe is to identify and help the movement of compounds in the early stages of development in order to increase the chance of a positive outcome. Within Europe, I am proud to pronounce, that Beerse is the largest team, next to Val de Reuil (France) and Toledo (Spain). Both Europe and the US have experts that the other teams need, and this is why it is important to communicate in an open way.
CREATe has four strategic areas namely: core scientific technologies, molecular sciences, integrative system Biology and translational sciences. The first area, core scientific technologies, registers every molecule that has ever been synthesized within Janssen. It is the goal of CREATe to further complement this library. The second area of molecular sciences tries to make it easier to find the right couple the right target substances to the corresponding diseases. Integrative system Biology is the third area, where tests are developed in order the research the effects of a molecule. The fourth and last area is translational sciences. Here the capacity is tested, with which a molecule will be accepted by the body and the improvement of the safety of a chemical molecule.
These four areas are important to secure a safe future for the patients, and new ideas are getting harder to come up with. Do you think you can come up with some possibilities for future drugs or improvements?
Durability
The hard times of today me never make us forget about the future. Durability is a very important goal for that matter. This is why Janssen Pharmaceutics created the Sustainability Council that is committed to promote a sustainability entrepreneurship. Every project has three different parts: an environmental part, a social part and, of course, an economic part. Not only does every project aims for these three goals, it aims to get in every division. In order to do so, every division is represented by a responsible, such as the IT-group, which can help to get the initiatives to the right persons. For already a long time, Janssen has been in the possession of solar panels and windmills, but a lot of people just do not know it. Another example is the reuse of the rinse water from the washing department, even up to three times! The large amount of plastic cups are even more durable than the reusable coffee mugs that have to be washed every time.
As a plan of action, the first step is to list everything that is already taken into account, such as the solar panels, windmills, recycling of rinsing water and the use of plastic cups. Secondly, these actions need to be clarified to the employees, and this is where we are now. The three musketeers are present in every alley and make the employees of Janssen aware of what is going on, and what they can do to help. It is important to know that every little step counts, and you have to begin with yourself. Only by taking responsibility for the present and future generations, will Janssen be able to maintain the strong role it is laying now.
To limit the ecological footprint, the use of water, energy and other raw materials need to be monitored. An important difficulty is that purification of water and waste treatment costs a lot of energy and money. So by limiting the amount of waste and water, it is not only advantageous for the environment, but it is also cheaper for the company and it decreases the health risks of the employees because they do not have to use dangerous solvents or diluents. Next to this economic part, the social part is very important as well. This is linked because by making profit, it is possible to make new drugs, new developments and get the drugs to the patients on time.
Motilium
This is a post as a reaction to what has been on the news concerning the drug ‘Motilium’. The EMA (European Medicine Agency) has started an investigation to the drugs that consist of domperidone as an active substance. The most well-known drugs is Motilium, which is used to treat nausea, vomiting, a bloating feeling and an upset stomach. These drugs might have a connection to heart diseases, and the FAGG (‘Belgisch Federaal Agentschap voor Geneesmiddelen en Gezondheidsproducten’) or FAMHP (Federal Agency for Medicines and Health Products) has asked for this investigation.

A “Product Issue Management Team” has been established with the goal to work close with the European authorities to help the ongoing research as efficiently and minimal disturbance for patients, clients and healthcare professionals as possible. This makes it possible to maintain the daily affairs of Janssen EMEA. This team strives to have no secrets, and will communicate on time and consistent to all who need the information. Important to know, is that this intervention will take a few months, and if you take your drugs as prescribed in the information leaflet.
Johnson & Johnson Consumer NV, a division of the same group of American companies that also include Janssen Pharmaceutics, still has faith in a positive benefit-risk ratio of the drug, and fully supports the European and Belgian producers of the drugs and will fully cooperate with the investigation.

Johnson and Johnson (J&J) are aware of the problems concerning domperidone, and are already following this for several years and will be passed to the regulators. Since 2011, they are performing two studies in collaboration with the FAMHP. One of these studies was concerning a cardiovascular safety study, which has been completed and that will be published this year. The company has already announced that the results where reassuring. The second study is investigating the link between domperidone and the cardiovascular effects and will be finished at the end of this year. A last remark is that J&J want to make sure that drugs containing domperidone will have to require prescription. If this will be the case will be announced at the end of April.
Move for Africa
Although this is a period of crisis and sometimes even devices get sabotaged by people who got fired, Janssen Pharmaceutics is still committed for development Cooperation’s where they want to help the population. A perfect example is ‘Move for Africa’ by La Libre Belgique, because they have the same vision as Janssen Pharmaceutics: making a durable and tangible difference for the world. Move for Africa is a Walloon organization that stands for awareness campaigns and this with the support of the Walloon Minister of Education. They try to promotion the development cooperation and humanitarian aid to Africa, especially to the students of the 5th grade of the secondary schools in Wallonia. During this Easter holydays, about hundreds to hundred and fifty students, or ten classes, will elaborate concrete development projects in different African countries. They will collect money, which will fully go to these projects.

Doing this, makes young people aware that there are different aspects to development Cooperation’s. Janssen Pharmaceutis is one of the project promoters and partners, which want to learn the students, what their responsibility is as a citizen of the world, thereby stimulating them to cooperate to the development of a democratic society.
Janssen feels responsible for and involved in the future of the youth, thus it wants to sensitize them in order to make fully committed to work for a better world, the future of our children. Secondly, they want to make them enthusiast for a scientific career, since they are the generation that have to answer the challenges of today and tomorrow. Therefore it is highly appreciated when a student invests its time, talent and energy in a sustainable world and accordingly in projects such as Move for Africa.
For more information, be sure to visit the website of Move for Africa: http://moveforafrica.lalibre.be/
Budgets
In the field of research and development (R&D) a lot of investments are necessary. As explained in the blog of ‘maintenance’, saving are done as much as possible. For my thesis I test whether the XBridge column (± 6000€) can replace the SunFire column (± 5000€). This is a difference of approximately 1000€ but the lifetime of this column is higher. How long will be tested by recording how many times the column is used until the column no longer provides good separations. Although a present investment of 1000€ in this column can eventually lead to savings over a certain period. In order to get the opportunity to test something, everything needs to be requested in advance, motivated why it could be necessary and tested for its usefulness. This is what I am testing at the moment. Firstly the tests are done on a small scale, namely analytical separations, wherefrom the translation can be done to the larger scale or preparative separations.
Another advantage of the XBridge, is the availability of an XBridge XP column which can result in a shorter time of analysis. This means that more purifications can be done. But we bumped into the limiting factor of solubility. The column was not able to reach the necessary flow rate and overpressure made the HPLC to go in shut down. The first choice was to ask for a Ultra high Pressure (Performance) Chromatography or UPLC device, but this application was rejected. Thus another solution needed to be made and this was changing the methods and discussing this problem with the manufacturer of the column, a reduction of five minutes can be made so far. This might not seem much, but five minutes per test can be a great difference if you know that about ten to twenty tests are done every day. Testing this further, based on trial and error, there is a possibility for an even greater reduction in time.
A small announcement for those of interest. On Sunday the 17 of March it is the international day of care. During this day, Janssen will organize an open house at which everyone is welcome from 10 to 15 in Beese Turnhoutseweg 30.
Reorganization
Reorganization is a common way for companies to save money and prevent bankruptcy. Since the year 2001, Janssen Pharmaceutics is forced to reorganize, and it still going on now. As a cause of this, a lot of people lost their jobs, especially in the US. This is because employees are not as well protected as the unions protect the workers here in Belgium. When the reorganization reaches Belgium, the fired workers are let go over a certain period of time. The last victims of the reorganizations of 2001 unemployed since 2004. Sonja Willems, the managing Director of Janssen Pharmaceutics, managed to save more than half of the jobs when a great amount of people was fired during this period. First of all, there was a period in which employees could voluntary leave the company. As a compensation, they got a bonus. Afterwards, the people who were about to retire got their early retirement, and lastly some compulsory redundancies were made. These people were guided in their search of a new job and some of them found a new job within Janssen Pharmaceutics.
A more recent example is the closure of the division Springhouse in the US, that has been close entirely from one day to the next. To reduce panic, an emergency meeting was set up, but nothing could be clarified. Now, the staff of research and development (R&D) are afraid to lose their job as well. This is since the director cannot guarantee that the reorganization will not happen in Beerse, and in the past it has always been the R&D who got the hardest hit. a possible explanation is that the Board of Directors wants to evolve with the market and be innovative. In order to make this possible, a lot of new ideas and new ways of working are necessary. The R&D is very fragile in this way of thinking, due to the fact that this is the core where renewal is being explored and tested.
All this commotion results in stress on the work floor, and some are already looking for a different job. Some people, such as the security guards and cleaning services, are being replaced by external companies. These peoples contract is not as binding as the people working for Janssen directly. Thus when these people need to be fired, it is much easier and Janssen does not have any obligations towards these people. Another advantage is that this is much cheaper for Janssen as well.
All this is still the result of the crisis, but what can we do about it? How can we make sure we have certainty in the future? What can we do to make it better for our children?
Maintenance
The setup of the analytical HPLC consists of a Separation Module and a PDA detector from Waters, and a column selector of Alltech. Maintenance is an important and necessary feature for all machines, including these. Unfortunately, this is not a cheap necessity, pushing several companies to make the choice of doing as much as possible by themselves and delaying the maintenance. Although this is the case here, it is not always allowed. In other companies, every time the operator of a device tries to fix it, it needs to be written down in a logbook. This must be done, since the contract with the companies of the devices states that all maintenance is done by this firm. Thus trying to avoid a situation where an employee tries to fix their device but instead makes it worse. As in many cases, both approaches have their advantages and disadvantages.
A week ago, one of the HPLC devices, namely the Separation Module, broke down. Instead of taking samples from the vail and injecting these onto the column, the vail was filled and nothing was injected resulting in the most unusual chromatograms. Firstly some tests were done, in order to determine where the problem was situated and if it would be possible to fix it ourselves. The problem was not easy to fix and an operator from Waters was called who would come on the next available moment, which was four days later. This is another reason why some companies try to stall the maintenance, because during this period of waiting, no experiments can be performed, thus with the consequence of unhappy chemists who want to proceed their work. Although the problem was known, the maintenance was needed due to the lack of the right equipment. When the technician arrived, he had already ordered the necessary parts that had arrived earlier that day. These technicians are very well educated and know these machines as the back of their hand, which is not abnormal because they often come into contact with the same problems for the same devices. In addition, they know the companies and the people who work there and visit these companies several times a year for repairs.
As it was believed that there was a problem with the valves, all valves were replaced together with the injector needle, but the replacement of the injection syringe was required as well. During the tests for the valves, the technician noticed that this syringe had problems with the suction the solvent. This could be due to a gas bubble present in the tubes, that acts as a resistance or cushion preventing it from fully sealing.
It took about half an hour to replace all the very small, but very expensive valves and injection needle. Then the pressure was elevated to press the valves tightly into their position and afterwards a calibration of the needle is needed, since it was replaced. The device does this automatically, but it takes about ten to fifteen minutes. Thanks to unexpected problems and the absence of a syringe, which the employee of Waters needed to go and find in another building, the maintenance lasted longer than originally expected. Three hours later, the final test was done. A vail with water was weighed, set in position, an injection was done and the vail was weighed again. Thanks to the weighing test and monitoring of the pressure, it could be concluded that the vail was not filled anymore, but injection occurred as it should and the problem was solved.
Practical implementation of the analytical test
All devices and columns used, are purchased from ‘Waters’.
1 Pump
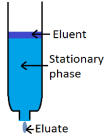
The pump used, is a constant flow pump. This pump uses two alternating pistons and the fluid chambers in positioned in series. The flow rate can be set at different values (ml/min). For the analyzes performed here, a flow rate of 2 ml/min is chosen. The higher the flow rate, the faster the test is done, but the higher pressure is needed to pump the mobile phase through the stationary phase.
2 Column
This has already been discussed previously. All the used columns (Hypersil BDS, SunFire and XBridge) are comprised of stainless steel, filled with a non-polar stationary phase C18. The dimensions and particle size are given below:
- Hypersil BDS C18 100 x 4.6 mm 3 µm
- SunFire C18 100 x 4.6 mm 3.5 µm
- XBridge C18 100 x 4.6 mm 3.5 µm
After use, the column is rinsed with a mixture of 50% acetonitril/methanol and kept at 100% methanol.
3 Injectionsystem, detector and recorder
This has already been discussed previously. An amount of 20 µl of the sample, is injected each time. For the detection, a mass detector is used in combination with a single wave length UV detector. The size of the signal that is detected and integrated or recorded on the chromatogram, is dependant of a set value. This is called an attenuation which can vary between 1 and 10. The greater this value, the more the recorded signal is reduced. After this has happened, the integrator will automatically create a list in which the retention time of each peak registered is printed for four different methods: the two buffers and two solvents previously mentioned.
4 Eluent
The type of solvent/eluent used, has an influence on the separation. The elution[1] can be done with the use of a single solvent or a mixture of solvents (isocratic) or changing the concentration of the different solvents (gradient).
When an isocratic elution is used, the composition of the mobile phase is constant during the entire analysis. The ideal composition of the different solvents is one at which all products are eluted within an acceptable period. For components that are fast eluting, it is possible that the separation is insufficient, whereas slow eluting components can cause peak widening. A solution for this problem is the use of a gradient elution (see figure), which means that there is a transition of a weak solvent, to a stronger solvent, which may lead to a shorter method time, better separation and higher sensitivity. One disadvantage is that after every analysis, the column needs to be brought back to the initial conditions. Another disadvantage is the presence of a dwell volume. This is the device dependent volume that the mobile phase needs to pass, from mixing, until reaching the column. This dwell volume, in combination with the volume of the column, influences the retention times. A smaller column, such as the analytical column, has a bigger effect on the retention times, than the bigger columns of the preparative size. This means that fast eluting components can elute, even before the gradient elution has started.
- The first period is the conditioning of the column, which takes about five minutes until the pressure is constant. During this period, the column will be brought in the conditions that is necessary for the separation of the monster. The appropriate condition for the actual, preparative separation can be chosen from the results of a smaller analytical test, with a sample of the monster.
- The second period, is the period at which the monster is sucked by the syringe and positioned for injected on the column. This takes about two and a half minutes.
- The last period, is the period of the actual separation. During this period, the first six minutes are crucial because the product is then injected and distributed over the column, and this is the period at which the pressure reaches its maximum. After the six minutes, separation and detection takes place and a report is made.
The detector and packing influence the choice of the solvent:
- in an apolar stationary phase, a polar solvent is needed
- the eluent should not interfere with the detection
The eluent used consists of a mixture of two different buffers (acetonitril and ammoniumcetate).
[1] Elution: the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent
HPLC in practice
Background
Because liquid chromatography uses columns with a ‘large’ diameters and a small flow, it takes a long time before the mixture is separated and the product can be collected. As we know now, a HPLC can be a possible solution to this problem. In short, a mixture is passed over a stationary phase with a high pressure, which results in some conditions for the stationary phase. Since the migrating components of the mixture each have different polarities and size, they also have different migration speeds.
Set-up
A HPLC system includes next five elements:
1. A liquid supply system: this is a pump that can generate a high pressure, and one or more water reservoirs
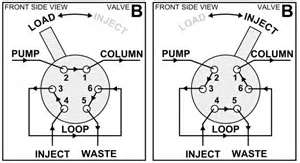
2. An injection system: typically this is a set-up as given in figure 1. This system is made out of stainless steel with different gates and a movable Teflon ring in the middle, which makes it possible to alternately connect two different external gates. In the load position, the mobile phase is loaded on the column by filling the loop with the sample. In the inject position, the sample is dragged to the column.
3. A column: these are mostly made of stainless steel with a more polar mobile phase than stationary phase.
4. A detector: after the mobile phase leaves the column, it passes through a detector for registration of the chromatogram. This detector has a great sensitivity (µg – ng), and there are different ways for detection:
- Ultraviolet-visible light detector, with constant or variable wavelength
- Fluorescence detector
- Breaking detector
- Electrochemical detector
5. A recorder: this is mostly linked to the computer, which analyses and interprets the data immediately
Quantitative analysis
When doing a quantitative analysis, using a HPLC, the method of internal standards is often used. This means that a known amount of a certain substance (internal standard) is added to the calibration sample and the sample that needs to be analyzed. The internal standard undergoes the same processes as the sample, it is injected in the same way and is similarly chromatographed. Because of this, next problems can be detected and registered:
- Inaccuracies in the making of the standard solutions
- Variations in injection volume or temperature of the column
- Drift of the detector signal for both the component that needs to be determined, as the internal standard
A correction for these problems can be done by determining the ratio of the signal of the component that needs to be analyzed and the internal standard. The certain substance, which is the internal standard, must meet certain conditions
- The registered signal and the component to be analyzed should be approximately the same size
- The behavior and detection must coincide with those of the component to be determined without interference from the conditions occurs. Thus, the retention time (tr) of the internal standard is not allowed to vary too much, without, however, overlapping those of the component
To do a quantitative analysis, a calibration curve is prepared, with on the X-axis: the concentration of the component to be determined, and on the Y-axis: the ratio of the component signals of an internal standard. The signals form peaks, wherefrom the surface area and height can be calculated. If the concentration of the internal standard is known exactly, next calculation are possible:
Qc / Qi = (Ac ⁄ As,c ) / (Ai ⁄ As,i ) = As,i / As,c * Ac / Ai
With:
- Qc and Qi : the concentration of the component to be analyzed and internal standard respectively
- Ac and Ai : the peak area of the component to be analyzed and internal standard respectively
- As,c and As,i : the specific surface area of the component to be analyzed and internal standard respectively (specific surface area = area per concentration of the injected material)
For a certain combination of the component to be analyzed and internal standard
As, i / As, c = constant = b
Which results in: Qc / Qi = b * Ac / Ai
Which is the equation of a straight line, and because the concentration of the internal standard is constant for every sample (Qi = constant), it can be concluded that:
Ac / Ai ~ Qc
If the basis of the registered peaks are constant, the peak area is directly proportional to the peak height which means that:
Hc / Hi ~ Qc
With Hc and Hi : peak height of the component to be analyzed and internal standard respectively.
This means that it is not necessary to know the concentration of the internal standard exactly, as long as the added amount thereof is always exactly the same.